
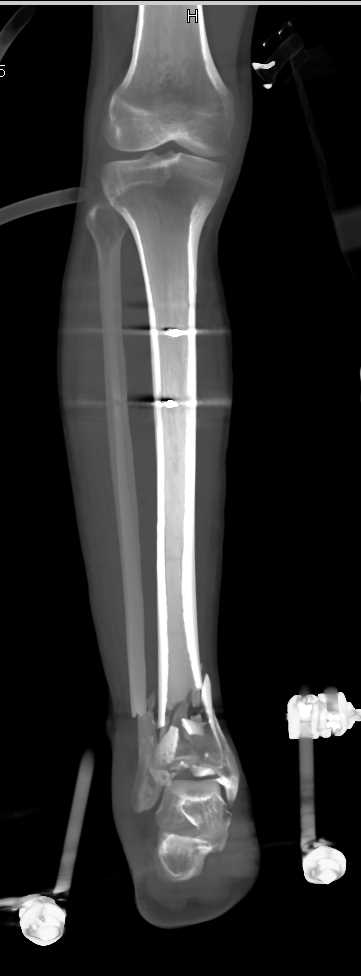
Plain radiographs are vital as they can identify fibular fractures, fibular shortening, and any abnormal spacing between the tibia and fibula caused by syndesmotic disruption. Obtaining images at the initial visit is important to rule out a Maisonneuve fracture. Figure 2b: External Rotation Stress Test.When both physical exam findings are present, Maisonneuve fracture is to be suspected. Proximal fibular tenderness suggests fracture. If there is tenderness with external rotation, syndesmotic injury is probable ( Figure 2b). Additionally, one can perform an external rotation stress test which has the foot start in a neutral position followed by external rotation of the tibia. The “Squeeze Test” requires palpation of the tibia and fibula at the mid-calf level and if it returns positive for tenderness, it suggests a syndesmotic injury ( Figure 2a). Patients may only report ankle pain with significant swelling, but it is important to examine the joints above and below the ankle. Patients may recall a twisting motion to their ankle but not always. Physical Exam:įor all patients with ankle injuries, it is extremely important to rule out a Maisonneuve fracture. Lastly, as the force is traveling through the deltoid ligament and medial malleolus, up towards the syndesmotic ligaments and interosseous membrane, the force generated exits the proximal fibula via fracture. Acting as a wedge, the talus places pressure on the lateral malleolus and causes syndesmotic disruption between the tibia and fibula. The talus externally rotates and applies stress to the medial aspect of the ankle and may cause deltoid ligament rupture or medial malleolus fracture. This extreme force places significant strain on the bones and ligaments that make up the ankle joint and often results in instability. Maisonneuve fractures are a result of external rotation of a planted foot, most often with pronation of the foot. Figure 1b: Anterior Anatomic View of the Lower Leg.Figure 1a: Medial and Lateral Anatomic Views of the Ankle.The articular surface of the ankle is formed by the joining of the superior surface of the talus, medial malleolus of the tibia, and lateral malleolus of the fibula ( Figures 1a-b). When disrupted the patient will experience instability in their gait, with possible pain and the potential to develop early osteoarthritis. The ankle provides stability while adapting to the surface one walks on and allows for the ability to invert, evert, plantarflex, and dorsiflex the foot. The ankle joint is composed of the distal tibia and fibula, and talus, connected by several soft tissue attachments. This injury is extremely important to not miss in the emergency department as it can result in poor outcomes if left untreated. There is limited information available in the literature regarding this fracture pattern, but it is believed to occur more often than what is reported. By applying external rotation to the foot, many of the stabilizing structures of the ankle are at risk of injury. In 1840 Jacques Gilles Maisonneuve, a French surgeon, described the fracture pattern through cadaveric studies that is now named after him. Fried, Brian Gilmer, MD, Stephen Knecht, MD Introduction:
#Closed fracture of distal end of right fibula full#
The lateral collateral ligament joins the femur and fibula, so whilst not as important as the other collateral ligaments, if damaged, it has a high co-incidence of stiffness or pain in other areas such as knee, ankle and foot can delay full rehabilitation.Home » Patient Info » Conditions and Procedures » Foot & Ankle » Maisonneuve Fracture Maisonneuve Fracture Jordan W.
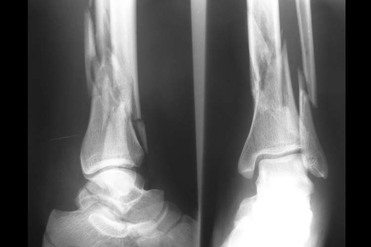
Although rare, these can occur in older adolescents with closed physes.Įnsure associated nerves ( common peroneal if the fibular neck is fractured), arterial territory (the anterior tibial pulse) and lateral collateral ligament is intact with normal function. These do poorly with conservative treatment, meaning the ankle must be imaged in those with an apparently isolated fracture of the fibula to prevent a missed tibial fracture. Be suspicious of an isolated spiral fracture at the proximal fibula it may be associated with a distal tibia fracture, called a Maisonneuve fracture. Compartment syndrome is a risk, but is more relevant if there is an associated tibial fracture. As with any fracture, union issues (delayed, malunion and non-union) is a risk, made worse if there’s infection.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
