

Pacemaker av sequential ekg code#
The revised NASPE/BPEG generic code for antibradycardia, adaptive-rate, and multisite pacing.
Pacemaker av sequential ekg full#
Biventricular ICDs ( CRT-D): an ICD with biventricular pacing option.Ī full list of pacemaker indications can be read in the ESC guidelines on cardiac pacing.New biventricular ICDs have 3 leads: an atrial lead, a left ventricular lead and a right ventricular lead. All ICDs have optional pacemaker activity to treat bradycardias. ICDs can save lives in patients who have a high risk of ventricular arrhythmias. If this is not effective, a defibrillator shock is delivered, usually with 16-36 Joules of energy. Usually the first treatment is anti-tachy pacing (pacing at a rate +- 10% above the ventricular rate in ventricular tachycardia, which can convert the rhythm to sinus rhythm). ICDs are a separate category and usually not considered pacemakers although they do have a pacing function. ICD (Internal Cardioversion Device): This device can detect and treat Ventricular Tachycardia and Ventricular Fibrillation.They include echocardiography, finding the narrowest QRS, and invasive hemodynamic measurements with pressure and flow wires. Several optimizing methods are being evaluated to find the most effective pacing delay between left and right ventricles.
This cardiac resynchronization therapy can improve symptoms and survival in some heart failure patients. The lead pacing the left ventricle is usually positioned in the coronary sinus. Biventricular pacemakers ( CRT-P): Leads in both ventricles are present for synchronized contraction.DDDR: As above, but the pacemaker has a sensor that records a demand for higher cardiac output and can adjust the heart rate accordingly.DDD: The pacemaker records both atrial and ventricular rates and can pace either chamber when needed.This type of pacemaker is used in patients with a reliable sinus node, but with an AV-block. VDD: The pacemaker senses atrial and ventricular events, but can only pace the ventricle.VVI: The ventricles are paced, when the intrinsic ventricular rhythm falls below the pacemaker's threshold.AAI: The atria are paced, when the intrinsic atrial rhythm falls below the pacemaker's threshold.The revised NASPE/BPEG generic code for antibradycardia pacing Pacemakers can be categorized according to the NASPE coding system, that usually consists of 3-5 letters. 4.5 Failure of Appropriate Pacemaker Firing.4.4 Failure of Appropriate Inhibition, Ventricular.4.3 Failure of Appropriate Inhibition, Atrial.4.2 Failure of appropriate capture, ventricular.

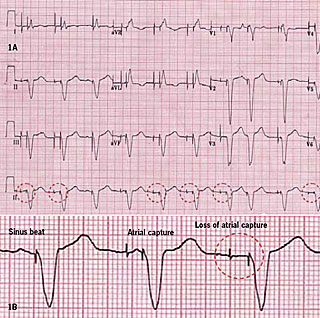
4.1 Failure of appropriate capture, atrial.3.1 Atrial-sensed ventricular-paced rhythm.Another exception is septal or RVOT placement of the pacing lead, which results in a less widened to normal QRS complex. An exception to this rule is left ventricular pacing in patients with congenital anomalies and patients with surgically placed epicardial pacemakers. As ventricular pacing occurs exclusively in the right ventricle the ECG shows a left bundle branch block pattern. In the second image the ventricles are paced directly, resulting in a ventricular paced rhythm. Accordingly the ventricular complex is delayed until the atrial signal has passed through the AV node. In the first example, the atria are being paced, but not the ventricles, resulting in an atrial paced rhythm. Usually these spikes are more visible in unipolar than in bipolar pacing. It shows pacemaker spikes: vertical signals that represent the electrical activity of the pacemaker. The pacemaker rhythm can easily be recognized on the ECG. A pacemaker is indicated when electrical impulse conduction or formation is dangerously disturbed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
